Researchers Improve Modeling to Protect Infrastructure from Earthquakes
Posted: Oct 9, 2023
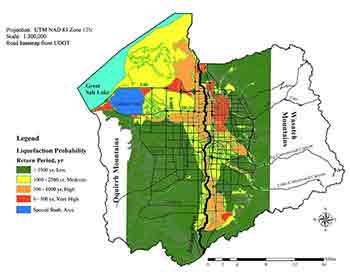 Liquefaction-induced ground failure and the resulting reduction in shear strength of soils occurring during major earthquakes has caused hundreds of millions of dollars of damage to transportation infrastructure such as bridges, embankments, culverts, and pavements. Researchers at the University of Utah are improving analytical and numerical methods to estimate the amount of permanent ground displacement associated with liquefaction-induced lateral spread. These methods will be used to make transportation more resilient to such damages and to proactively identify, quantify, visualize, prioritize, and mitigate risk from earthquakes. This Phase 1 project focused on collecting and organizing liquefaction information in a common and comprehensive database to provide all researchers with a substantially larger, more consistent, and more reliable source of liquefaction data than existed previously.
Liquefaction-induced ground failure and the resulting reduction in shear strength of soils occurring during major earthquakes has caused hundreds of millions of dollars of damage to transportation infrastructure such as bridges, embankments, culverts, and pavements. Researchers at the University of Utah are improving analytical and numerical methods to estimate the amount of permanent ground displacement associated with liquefaction-induced lateral spread. These methods will be used to make transportation more resilient to such damages and to proactively identify, quantify, visualize, prioritize, and mitigate risk from earthquakes. This Phase 1 project focused on collecting and organizing liquefaction information in a common and comprehensive database to provide all researchers with a substantially larger, more consistent, and more reliable source of liquefaction data than existed previously.
Steven Bartlett, Ph.D.
University of Utah
Development of Next Generation Liquefaction (NGL) Database for Liquefaction-induced Lateral Spread
MPC-22-477

